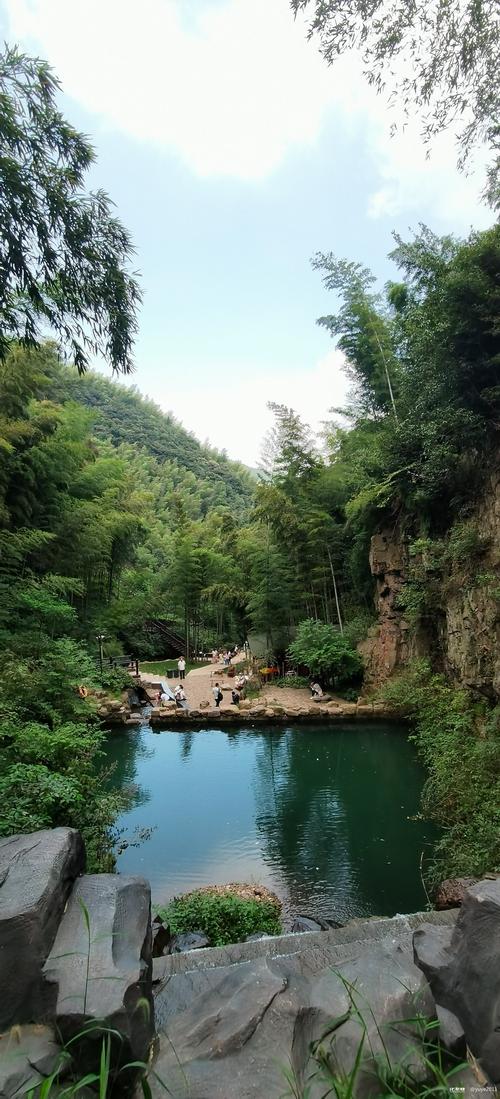
经典古镇游 —— 前黄古镇(宋庆龄故居)+ 西太湖花海
这条线路适合喜欢江南风情、慢生活和拍照的游客,车程短,内容轻松。

(图片来源网络,侵删)
- 主题: 感受古镇底蕴,邂逅浪漫花海
- 适合人群: 情侣、家庭、摄影爱好者
- 距离: 从常州市区出发,车程约30-60分钟
上午:前黄古镇 & 宋庆龄故居
- 简介: 前黄古镇是常州保存较为完好的古镇之一,没有过度商业化,充满了生活气息,核心看点是宋庆龄故居,这是一座典型的江南园林式建筑,环境清幽,古色古香。
- 游玩亮点:
- 宋庆龄故居: 参观这位伟大女性的生平事迹,欣赏精美的园林建筑和庭院。
- 古镇老街: 漫步在青石板路上,感受老常州的市井生活,可以品尝一些当地小吃。
- 悠闲氛围: 这里游客不多,非常适合放慢脚步,找个茶馆坐坐,喝杯茶。
- 游玩时间: 2 - 3小时
- 地址: 常州市武进区前黄镇
- 门票: 宋庆龄故居门票约20元,古镇本身免费。
中午:午餐
- 可以在前黄镇上找一家本地菜馆,品尝太湖三白(白鱼、白虾、银鱼)等特色菜,或者来一碗地道的加蟹小笼包。
下午:西太湖花海
- 简介: 西太湖是常州的后花园,沿湖风景优美,花海是西太湖景区的一大亮点,不同季节有不同的花海盛开(春季郁金香、夏季向日葵、秋季粉黛乱子草等)。
- 游玩亮点:
- 花海拍照: 在花海中拍照,非常出片,无论是个人照还是情侣照都很有感觉。
- 环湖骑行: 沿着西太湖的绿道骑行,吹着湖风,欣赏湖景,非常惬意。
- 龙城大桥: 可以开车或步行到龙城大桥上,从不同角度欣赏西太湖的壮丽景色。
- 游玩时间: 2 - 3小时
- 地址: 常州市武进区西太湖大道
- 门票: 花海区域通常免费进入,部分特殊展览或活动可能收费。
自驾小贴士:
- 路线简单,导航“前黄古镇”和“西太湖花海”即可。
- 花海季节性很强,出发前最好在网上查询一下当季是否盛开。
- 周末花海游客较多,建议早点去。
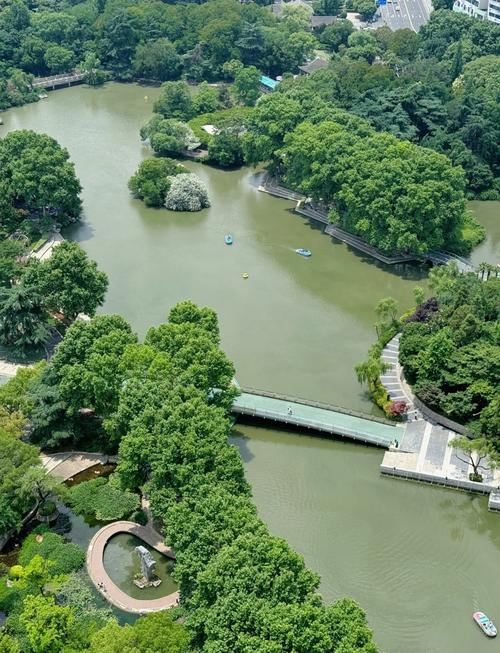
山水休闲游 —— 天目湖山水园
这条线路适合家庭出游,尤其是有老人和小孩的家庭,可以结合湖光山色和美食。
- 主题: 湖光山色,美食盛宴
- 适合人群: 家庭亲子、朋友聚会
- 距离: 从常州市区出发,车程约1.5小时
全天:天目湖山水园
- 简介: 天目湖是常州最著名的5A级旅游景区之一,核心是山水园,由湖区和山区组成。
- 游玩亮点:
- 乘船游湖: 必体验项目!乘坐游船,在碧绿的湖面上穿行,欣赏两岸青山,感受“天目湖”的意境。
- 山水园徒步: 园内空气清新,步道平缓,可以沿着湖边和山间小径散步,欣赏瀑布和竹林。
- 蝴蝶谷: 园内有一个蝴蝶谷,可以近距离观察各种美丽的蝴蝶,深受小朋友喜爱。
- 美食: 山水园出口附近就是著名的天目湖美食街,可以品尝到最正宗的天目湖砂锅鱼头,味道鲜美,营养丰富。
- 游玩时间: 4 - 5小时
- 地址: 溧阳市天目湖镇
- 门票: 约90元/人(含游船)。
自驾小贴士:
- 从常州出发,走沿江高速或常溧高速,在“天目湖”出口下,非常方便。
- 一定要提前预定好餐厅,尤其是周末,想吃砂锅鱼头最好提前去排队。
- 可以考虑把车停在景区门口的停车场,然后乘坐景区接驳车进入。
文化历史游 —— 淹城春秋乐园
这条线路非常适合对历史文化、主题游乐感兴趣的年轻人和家庭,尤其是有学龄儿童的家庭。
- 主题: 穿越春秋,体验游乐
- 适合人群: 年轻人、家庭亲子、历史爱好者
- 距离: 从常州市区出发,车程约40分钟
全天:淹城春秋乐园
- 简介: 这里是全球唯一以春秋文化为主题的梦幻乐园,它建立在春秋时期的淹城遗址之上,将历史文化与现代游乐设施完美结合。
- 游玩亮点:
- 五大主题区: 包括诸子百家区、百灵水世界、儿童天地区、九洲城和市井商街,每个区都有独特的游乐项目和表演。
- 大型设备: 有“孙武点将台”、“九龙问鼎”等刺激的过山车和大型设备。
- 文化演艺: 园区内有编钟乐舞、战马表演等充满春秋气息的演艺活动,非常精彩。
- 遗址公园: 紧邻乐园的淹城遗址公园是免费的,可以参观古老的子城、子城河,感受3000年的历史沧桑。
- 游玩时间: 4 - 6小时
- 地址: 武进区武进大道
- 门票: 门票约180元/人,部分项目需要另外付费或购买通票。
自驾小贴士:
- 园区停车场很大,停车方便。
- 园区很大,建议穿一双舒适的鞋子。
- 下载官方APP,可以查看地图、表演时间和排队情况,方便规划路线。
江苏“小九寨” —— 宜兴竹海
如果您想彻底远离城市喧嚣,拥抱大自然,宜兴竹海是绝佳选择。
- 主题: 漫步竹海,吸氧洗肺
- 适合人群: 自然风光爱好者、徒步爱好者、摄影爱好者
- 距离: 从常州市区出发,车程约1.5小时
全天:宜兴竹海风景区
- 简介: 这里是中国著名的“竹海”,拥有近万亩的翠竹,山峦叠翠,风景如画,被誉为“江苏的张家界”。
- 游玩亮点:
- 索道观景: 乘坐索道上山,可以从空中俯瞰整个竹海的壮丽景象,非常震撼。
- 步行栈道: 沿着山间的木栈道徒步,穿梭在竹林中,听着风吹竹叶的沙沙声,非常惬意。
- 玉女峰: 江苏第二高峰,登顶可以远眺群山。
- 镜湖: 一个清澈的人工湖,倒映着周围的竹林和山峰,景色如画。
- 游玩时间: 3 - 4小时
- 地址: 宜兴市湖㳇镇
- 门票: 约80元/人,索道另收费。
自驾小贴士:
- 山路较多,自驾请谨慎驾驶。
- 穿防滑性能好的鞋子,山路有些湿滑。
- 可以带上水和一些零食,山上补给点较少。
总结与建议
| 方案 | 主题 | 亮点 | 适合人群 | 自驾距离 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 方案一 | 古镇花海 | 古镇清幽,花海浪漫 | 情侣、摄影、家庭 | 30-60分钟 |
| 方案二 | 山水美食 | 湖光山色,鱼头汤鲜 | 家庭亲子、美食爱好者 | 5小时 |
| 方案三 | 文化游乐 | 春秋主题,项目丰富 | 年轻人、家庭、学生 | 40分钟 |
| 方案四 | 竹海徒步 | 天然氧吧,风光秀丽 | 自然爱好者、徒步者 | 5小时 |
最后的小建议:

(图片来源网络,侵删)
- 提前查询: 出发前务必通过官方渠道或旅游APP查询目的地的开放时间、门票价格和防疫政策(如有)。
- 错峰出行: 尽量选择工作日出行,避开周末和节假日的高峰人流。
- 备好物品: 根据天气情况准备防晒霜、遮阳帽、雨具、舒适的鞋子等。
- 注意安全: 无论是在古镇漫步还是在山区游玩,都要注意人身和财物安全。
希望这些方案能帮助您规划一次愉快的常州周边自驾一日游!

(图片来源网络,侵删)